The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a standard model for data interchange on the web. It is a W3C recommendation and is used to represent information about resources in a graph-based format. RDF provides a way to describe resources on the web, such as web pages, digital images, and people, in a manner that is both machine-readable and understandable by humans. In this article, you will learn what is Resource Description Framework (RDF) and how to use it.
ALSO READ: How To Check Your Tim Hortons Gift Card Balance Canada?
What Is Resource Description Framework?
The Resource Description Framework, or RDF for short, is a standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) for describing data on the web [W3C RDF]. The purpose of the Resource Description Framework (RDF) is to provide a way to represent information about things (resources) on the web. This can include anything from physical objects like books and buildings to digital resources like web pages and scientific data.
What Does Resource Description Framework Mean?
The term “Resource Description Framework” (RDF) refers to a standardized model for describing resources on the web or in other information systems. RDF provides a structured and flexible way to represent metadata about resources, including web pages, digital documents, and various types of data.
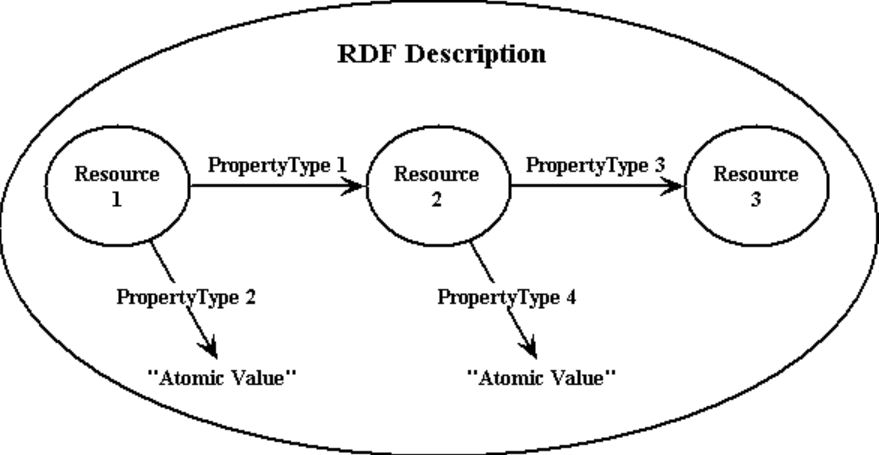
In RDF, information is organized into triples, which consist of three parts: subject, predicate, and object. These triples form statements that describe relationships between resources. The subject represents the resource being described, the predicate represents a property or attribute of the subject, and the object represents the value of that property.
RDF enables data to be expressed in a format that is both machine-readable and understandable by humans. It is a key technology for the Semantic Web, facilitating the integration and sharing of data across different applications and domains. By providing a common framework for describing resources and their relationships, RDF helps to enable interoperability, data integration, and knowledge discovery on the web.
How To Use Resource Description Framework (RDF)?
Using Resource Description Framework (RDF) involves understanding its core concepts and leveraging tools to create and work with RDF data. Here’s a breakdown of how to get started:
Understanding the Basics:
-
Triples: RDF represents information using “triples,” which are statements with three parts:
- Subject: The resource being described (e.g., a book, a person)
- Predicate: The relationship between the subject and the object (e.g., “is written by,” “lives in”)
- Object: The value that describes the subject based on the predicate (e.g., an author’s name, a city)
-
Serializations: RDF data itself isn’t human-readable. It’s written in specific formats called “serializations.” Common ones include:
- Turtle (TTL): A human-readable format using keywords like “@subject” and “@predicate.”
- RDF/XML: An XML-based format for structured data exchange.
- JSON-LD: A JSON-based format for embedding RDF data within web pages.
Learning the Tools:
-
RDF Editors: These tools help you create and edit RDF data in your chosen serialization format. Popular options include:
- Protege: A free, open-source ontology editor with built-in RDF editing capabilities.
- TopBraid Composer: A commercial RDF editor with advanced features for complex knowledge graphs.
-
RDF Query Languages: Once you have RDF data, you can use query languages to retrieve specific information. A common option is SPARQL (SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language), which allows you to query RDF data using a syntax similar to SQL for querying databases.
Putting it into Practice:
There are various ways to use RDF depending on your goals:
- Sharing Data: Use RDF to describe data about your products, research findings, or any other information you want to share with others in a way that’s machine-readable and interoperable.
- Building Knowledge Graphs: Connect related data points using RDF triples to create a knowledge graph, which can be used for tasks like information retrieval and recommendation systems.
- Semantic Web Development: Contribute to the development of the Semantic Web, where machines can understand and reason about information on the web using RDF as a foundation.
Learning Resources:
- W3C RDF Tutorial: https://www.w3.org/RDF/
- RDF Tutorial (YouTube video): [YouTube RDF Tutorial]
- Online RDF editors and tools can be found with a web search for “RDF editor.”
Image Courtesy: medium